PS is a thermoplastic polymer. Polystyrene (PS) is an aromatic polymer made from the monomer styrene and can be rigid or foamed. Standard polystyrene is clear, hard and brittle. The resin is very inexpensive per unit weight. It builds a rather poor barrier to oxygen and water vapor and has a relatively low melting point. PS is one of the standard materials conventionally used in the life sciences, partially due to its relatively low price. Microtiter plates, for example, are usually made from PS.
Grades:
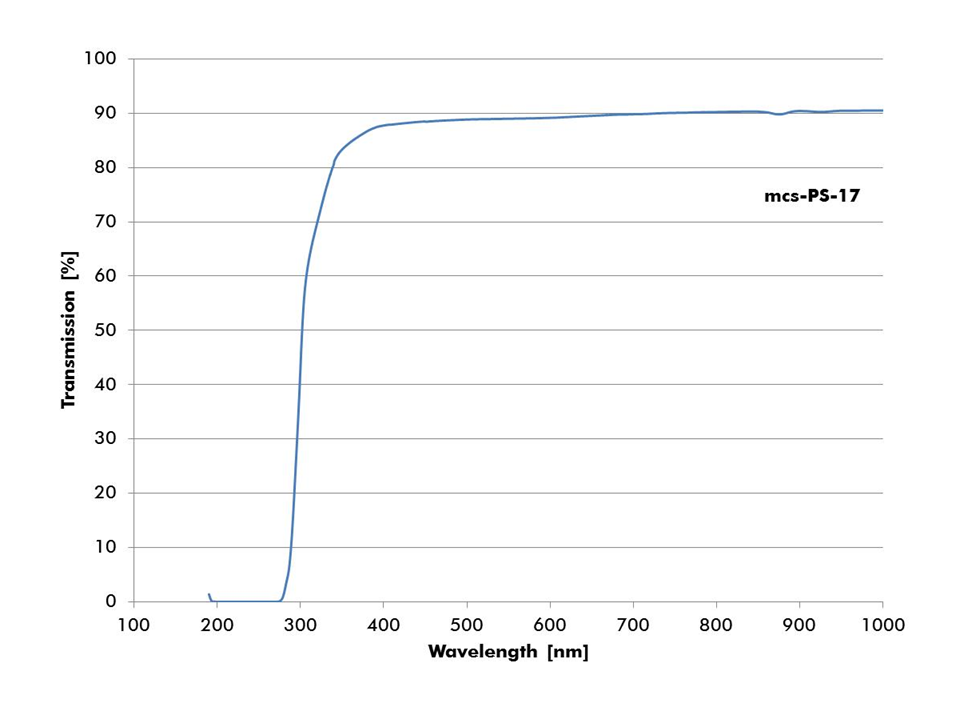
mcs-PS-17 – Tg: 100°C
mcs-foil-095 – 125µm Thickness, Tg: 100°C
PS can be used with:
- Bases
- Butyl Alcohol, Ethylene Glycol
- Organic Acids like Citric Acids, Formic Acids, Tartaric Acids
- Diluted Inorganic Acids at Lower Temperatures (except Hydrofluoric Acids)
- Mineral Oils
- Hydrogen Oxide
PS cannot be used with:
- Ketones
- Esters
- Ethers
- Halogenated Organic Reagents
- Hydrocarbons (except Mineral Oils)
Transmission Spectrum of 1.0 mm thick Microscopy Slide of mcs-PS-17